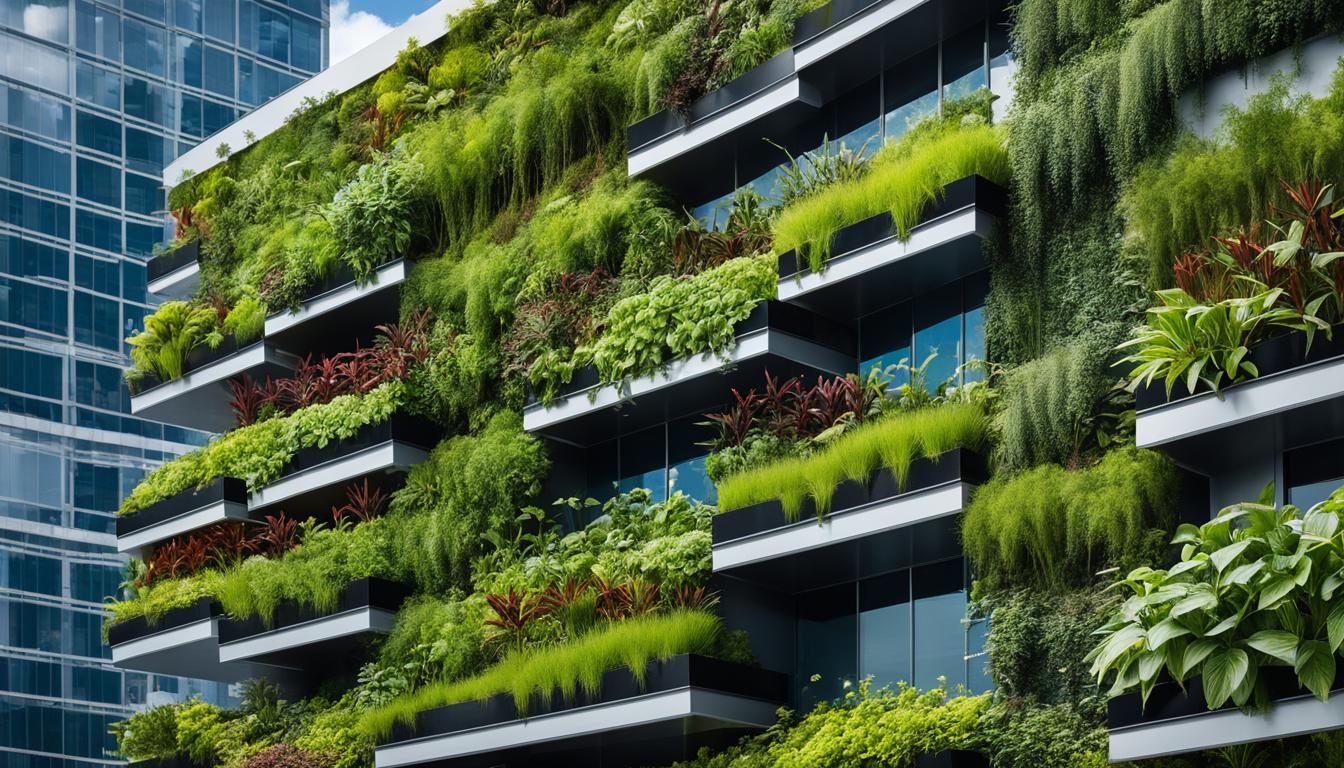
Green roofs and living walls are innovative concepts that are being integrated into green building and architecture to enhance sustainability and energy efficiency. These features offer a multitude of benefits, including improved air quality, reduced energy costs, enhanced biodiversity, and stormwater management. By incorporating green roofs and living walls into their designs, architects, interior designers, and construction companies can create environmentally friendly and socially responsible buildings that contribute to a sustainable future.
Key Takeaways:
- Green roofs and living walls enhance sustainability and energy efficiency in green building and architecture.
- They offer benefits such as improved air quality, reduced energy costs, enhanced biodiversity, and stormwater management.
- Incorporating green roofs and living walls into designs promotes environmentally friendly and socially responsible buildings.
- Architects, interior designers, and construction companies can contribute to a sustainable future through the use of green roofs and living walls.
Note: The image shows a sustainable green building, representing the environmentally friendly and energy-efficient designs that can be achieved through the use of green roofs and living walls.
The Benefits of Green Roofs
Green roofs offer numerous economic, environmental, and social benefits. They are not only aesthetically pleasing but also contribute to a sustainable and energy-efficient future.
- One of the key economic benefits of green roofs is their ability to extend the lifespan of a roof. The vegetation layer acts as a protective barrier, shielding the roof from the elements such as UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and extreme weather conditions.
- Green roofs also provide substantial energy savings. The vegetation layer acts as insulation, reducing heating and cooling energy consumption in buildings. This can lead to significant cost savings on energy bills over time.
- Water management is another critical aspect of green roofs. They help manage stormwater runoff by absorbing a significant amount of rainwater. This reduces the burden on urban sewer systems and helps prevent flooding.
- In addition to economic benefits, green roofs have environmental advantages. They contribute to reducing air pollution by absorbing and filtering pollutants from the air. Green roofs also play a vital role in mitigating the urban heat island effect by reducing the surface temperature of buildings.
- Moreover, green roofs enhance urban biodiversity by creating habitats for birds, insects, and other wildlife in urban areas. They provide a green space in otherwise concrete-dominated landscapes, promoting the well-being of both humans and nature.
Overall, green roofs offer a range of benefits, including economic savings, energy efficiency, water management, air pollution reduction, and the promotion of urban biodiversity. Their implementation can have a positive impact on the environment, society, and the economy.
| Economic Benefits | Environmental Benefits |
|---|---|
| Extends the lifespan of a roof | Reduces air pollution |
| Reduces heating and cooling energy consumption | Helps mitigate the urban heat island effect |
| Saves money on energy costs | Improves water management |
| Enhances urban biodiversity |
The Benefits of Living Walls
Living walls, also known as green walls or vertical gardens, offer numerous benefits that contribute to a sustainable and healthy built environment. These innovative features provide similar advantages to green roofs, such as improved air quality, enhanced energy efficiency, and increased biodiversity.
One of the key benefits of living walls is their ability to improve air quality. Through the process of photosynthesis, living walls absorb pollutants from the surrounding environment and release oxygen, creating a fresher and healthier atmosphere. This can have a significant impact on indoor air quality, particularly in urban areas where pollution levels are high.
In addition to improving air quality, living walls contribute to energy efficiency. Their dense vegetation acts as an insulating layer, reducing heat transfer and lowering the need for heating and cooling systems. This can lead to significant energy savings and a more sustainable use of resources.
Moreover, living walls provide a habitat for various species, promoting biodiversity in urban areas. By creating green spaces vertically, these walls become a source of food, shelter, and nesting grounds for birds, insects, and other wildlife. They form a vital part of urban ecological networks, supporting the conservation of native species and enhancing the overall ecological balance.
The integration of living walls in building design not only improves environmental aspects but also enhances the aesthetics and well-being of the surrounding area. The vibrant colors and textures of the vegetation create visually appealing facades, transforming concrete jungles into green oases. Studies have shown that exposure to nature has positive effects on mental health and overall well-being, making living walls a valuable addition to any urban setting.
“Living walls contribute to improved air quality, enhanced energy efficiency, and increased biodiversity.”
Living Walls Benefits Overview:
- Improved air quality through pollutant absorption and oxygen release
- Enhanced energy efficiency by acting as an insulating layer
- Increased biodiversity by providing habitats for birds, insects, and wildlife
- Improved aesthetics and well-being in urban areas
Living walls are becoming increasingly popular in sustainable building and architecture due to their numerous advantages. Whether as standalone features or in combination with green roofs, these vertical gardens play a crucial role in creating healthier, more energy-efficient, and visually appealing built environments.

Types of Green Roofs
Green roofs come in various types, each with its own unique features and applications. Understanding the different types can help architects and designers choose the most suitable option for their projects. The three main types of green roofs are:
-
Extensive Green Roofs
Extensive green roofs have a shallow growing medium, typically ranging from 2 to 6 inches in depth. This type of green roof is low-maintenance and lightweight, making it ideal for retrofits and buildings with limited load-bearing capacities. Commonly used plants for extensive green roofs include sedum, grasses, and mosses.
-
Intensive Green Roofs
Intensive green roofs have a deeper growing medium, usually more than 6 inches in depth, allowing for a wider variety of plant species, including trees and shrubs. This type of green roof requires more maintenance and is suitable for larger buildings with higher load-bearing capacities. Intensive green roofs provide more opportunities for recreational spaces, gardens, and even urban farming.
-
Semi-Intensive Green Roofs
Semi-intensive green roofs strike a balance between extensive and intensive green roofs. They feature a moderate-depth growing medium, typically around 6 inches in depth. Semi-intensive green roofs offer more plant choices than extensive green roofs while requiring less maintenance compared to intensive green roofs. This type of green roof is versatile and can accommodate a variety of plant species, including grasses, perennials, and small shrubs.
Architects and designers can consider the specific requirements of their projects, such as structural limitations and desired aesthetics, when selecting the type of green roof to incorporate into their designs.
Implementing Green Roofs and Living Walls
Implementing green roofs and living walls requires careful planning and consideration to ensure their success and long-term performance. Several key steps need to be followed to effectively integrate these sustainable features into a building or landscape project.
Assessing Feasibility
Before proceeding with the installation of green roofs or living walls, it is essential to assess the feasibility of the project. Factors such as structural capacity, building codes, and local regulations should be evaluated to determine if the site is suitable for implementing these green solutions.
Selecting the Right System
Choosing the appropriate green roof or living wall system is crucial for achieving the desired outcomes. Considerations include the project’s goals, budget, and maintenance capabilities. Assessing the site’s location, climate, and exposure to sunlight will help determine the most suitable system for optimal performance.
Plant Selection
The selection of plants for green roofs and living walls is a critical aspect of their implementation. Native plant species that are well-adapted to the local climate should be prioritized to ensure better resilience and reduced maintenance requirements. Consulting with a horticulturist or landscape architect can help in choosing the right plant palette.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation of green roofs and living walls is essential to ensure their longevity and functionality. Hiring experienced professionals who specialize in these systems is recommended to ensure proper installation techniques are followed. Regular maintenance, including irrigation, pruning, and weed control, is vital to preserve the health and aesthetics of these green features.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Monitoring the performance of green roofs and living walls is crucial to assess their effectiveness and identify any issues that may arise. Regular evaluation of factors such as plant health, stormwater management, and energy savings can provide valuable insights into the success of the project. Monitoring systems and technologies can be implemented to track and analyze key metrics.
By carefully implementing green roofs and living walls, architects, landscape designers, and building owners can create sustainable and environmentally conscious spaces that promote biodiversity, enhance energy efficiency, and contribute to a greener future.
| Implementing Green Roofs | Assessing Feasibility | Selecting the Right System | Plant Selection | Installation and Maintenance | Monitoring and Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ensure compliance with local regulations | Evaluate structural capacity and building codes | Consider project goals, budget, and maintenance capabilities | Choose native plant species adapted to the local climate | Hire experienced professionals for proper installation | Monitor plant health, stormwater management, and energy savings |
| Assess site suitability | Evaluate local regulations | Consider location and exposure to sunlight | Consult with horticulturist or landscape architect | Regular maintenance including irrigation and pruning | Implement monitoring systems and technologies |
Inspiring Examples of Green Roofs
Green roof projects around the world showcase the aesthetic and environmental benefits of incorporating green roofs into architectural designs. These inspiring examples demonstrate how these eco-friendly features can enhance sustainability and create beautiful spaces.
ACROS Fukuoka Prefectural International Hall
The ACROS Fukuoka Prefectural International Hall in Japan is renowned for its terraced green roof that seamlessly integrates with the surrounding landscape. This innovative design not only provides a visually stunning green space but also contributes to reducing urban heat island effect and improving air quality.
Brooklyn Botanic Garden Visitors Center
The Brooklyn Botanic Garden Visitors Center in New York City features a captivating green roof that harmonizes with the natural beauty of the botanical garden. This living roof not only enhances the aesthetics of the building but also provides insulation and reduces stormwater runoff, contributing to a more sustainable urban environment.
California Academy of Sciences
The California Academy of Sciences in San Francisco boasts a remarkable living roof that covers approximately 2.5 acres. This green roof is home to more than 1.7 million native plants and helps regulate the building’s temperature, reducing the need for heating and cooling. It serves as a prime example of how green roofs can blend seamlessly with modern architectural designs while offering significant ecological advantages.
Changi Airport Terminal 3 Interior Landscape
The Changi Airport Terminal 3 in Singapore stands out for its incorporation of green roofs into its interior landscape. This unique feature not only creates a soothing and natural ambiance within the terminal but also contributes to air purification, energy conservation, and a pleasant airport experience for travelers.
Green Walls and Their Benefits
Green walls, including green facades, living walls, and retaining living walls, offer a multitude of benefits for both public and private spaces. These vegetated wall surfaces not only enhance the aesthetics of urban areas but also provide significant advantages related to air quality, energy efficiency, biodiversity, and noise reduction.
One of the key benefits of green walls is improved air quality. As plants photosynthesize, they absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, contributing to cleaner and healthier air. Green walls act as natural air filters, removing pollutants and particulate matter, which can enhance the overall well-being of individuals in urban environments.
Furthermore, green walls play a vital role in energy efficiency. By acting as natural thermal insulators, they can help regulate indoor temperatures. In warm climates, green walls can provide shade, reducing the need for excessive air conditioning and saving energy. Conversely, in colder regions, green walls can act as an extra layer of insulation, reducing heat loss and decreasing heating requirements.
In addition to their role in improving air quality and energy efficiency, green walls also contribute to increased biodiversity. These living ecosystems create habitats for birds, insects, and other wildlife, promoting biodiversity in urban environments. Green walls can serve as stepping stones for migrating animals and help restore natural habitats that may have been lost due to urbanization.
Furthermore, the inclusion of green walls in architectural designs offers marketing potential for businesses and organizations. The presence of green walls can attract customers and visitors, as they convey a commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility. Green walls provide a unique and visually striking feature that sets buildings apart, contributing to a positive reputation and brand image.
Green walls, with their numerous benefits, offer an innovative and sustainable solution for enhancing the aesthetics, air quality, energy efficiency, and biodiversity of urban spaces.
Overall, green walls are a valuable addition to green building and architectural designs. With their ability to improve air quality, increase energy efficiency, enhance biodiversity, and contribute to the overall well-being of urban spaces, green walls play a crucial role in creating sustainable and environmentally friendly environments.

Conclusion
Green roofs and living walls are essential components of green building and architecture, driving sustainable design and energy efficiency. These innovative features offer a wide range of benefits, including improved air quality, reduced energy costs, enhanced biodiversity, and effective stormwater management.
By incorporating green roofs and living walls into their designs, architects and designers can create eco-friendly and socially responsible buildings. The integration of these elements not only promotes a healthy environment but also contributes to a more sustainable future for our communities.
Through the implementation of green roofs, buildings can experience improved thermal insulation, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems and leading to energy savings. Additionally, the presence of green roofs and living walls helps to mitigate the urban heat island effect, enhance urban biodiversity, and create aesthetically pleasing and functional spaces.
As we continue to prioritize green building and sustainable design practices, the inclusion of green roofs and living walls remains a crucial aspect of achieving energy-efficient and environmentally conscious architecture. By harnessing the power of nature and leveraging these innovative solutions, we can create a greener, healthier, and more sustainable built environment.
FAQ
What are green roofs and living walls?
Green roofs are roofs that are covered with vegetation, while living walls refer to vertical gardens or green facades.
What are the benefits of green roofs?
Green roofs offer economic benefits, such as extending the lifespan of a roof and reducing energy costs. They also help manage stormwater runoff and improve air quality and urban biodiversity.
What are the benefits of living walls?
Living walls improve air quality, enhance energy efficiency, and contribute to increased biodiversity in urban areas. They also have aesthetic and marketing potential.
What are the different types of green roofs?
There are three main types of green roofs: extensive, intensive, and semi-intensive. Each type has its own characteristics and applications.
How do you implement green roofs and living walls?
Implementing green roofs and living walls involves assessing project feasibility, selecting the right system, choosing suitable plants, proper installation and maintenance, and ongoing monitoring and evaluation.
Can you provide examples of inspiring green roof projects?
Some inspiring green roof projects include ACROS Fukuoka Prefectural International Hall in Japan, the Brooklyn Botanic Garden Visitors Center, the California Academy of Sciences, and the Changi Airport Terminal 3 in Singapore.
What are green walls and what are their benefits?
Green walls encompass different types of vegetated wall surfaces, including green facades, living walls, and retaining living walls. They offer benefits such as improved air quality, energy efficiency, increased biodiversity, and noise reduction.
What is the role of green roofs and living walls in green building and architecture?
Green roofs and living walls play a significant role in promoting sustainability and energy efficiency in green building and architecture. They offer a range of benefits that contribute to a more environmentally friendly and socially responsible built environment.
Source Links
- https://greenroofs.org/about-green-walls
- https://www.asla.org/contentdetail.aspx?id=43536
- https://ugreen.io/the-green-revolution-how-green-roofs-and-living-walls-are-transforming-urban-spaces/
- Technical Analysis in Crypto: Master the Art of Cryptocurrency Trading - October 1, 2024
- Fundamental Analysis for Crypto - September 30, 2024
- Day Trading vs. Long-Term Investing: Understanding the Dynamics of Cryptocurrency Trading - September 28, 2024